HITs, Journeys and Tasks
Here we define the nomenclature used within Covfee to talk about online experiments and their sub-parts.
The HIT
The main unit in Covfee is possibly the HIT (Human Intelligence Task). Despite the name, in crowd-sourcing settings the term HIT is often used to denote multiple tasks performed by an annotator or experiment subject. What distinguishes the HIT is that it is independent of any other HITs and it cannot be (or may not be convenient to) split into independent sub-units. Each HIT is normally identified by a single URL and is paid when completed. In Covfee we generalize this idea by using the term HIT to denote one or more tasks performed by one or more experiment subjects or annotators. For example, a HIT may be an online video conversation, or a game of chess to be completed by two people. The same HIT may include separate demographic questionnaires and post-experiment questionnaires for both participants.
In covfee, a HIT is specified via it's graph structure. Our videocall example can be drawn as follows:
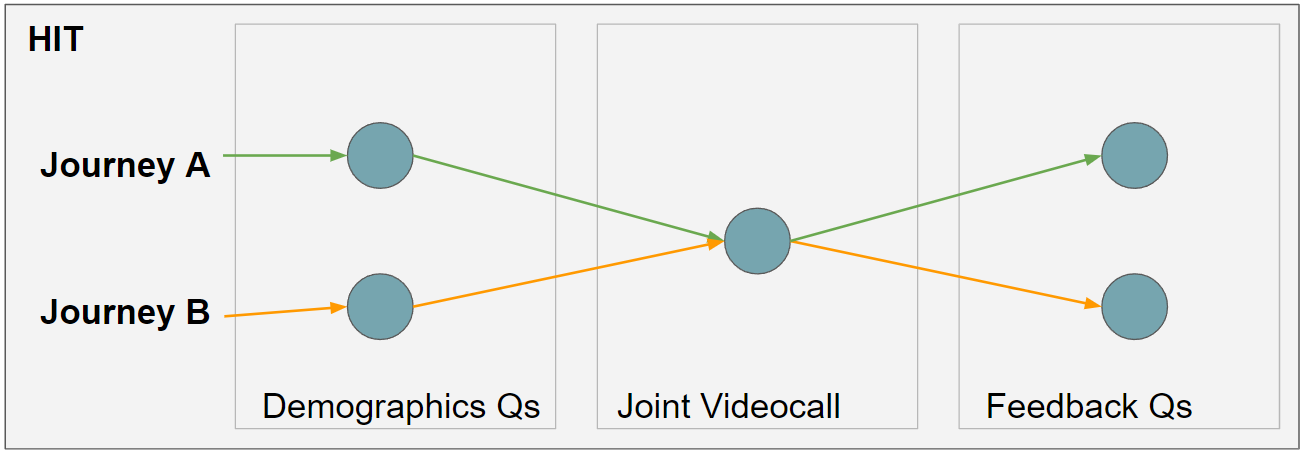
A HIT is composed of one or multiple Tasks, and one or multiple Journeys or paths through the Tasks. In Covfee, these paths must be acyclic but may be assymetric (ie. subjects may follow different paths). Each Journey is mapped to a URL by Covfee, which when opened accesses the current node/task for that HIT. In most cases tasks are to be completed in order.
Usinc Covfee consists in specifying one or multiple HITs. Once done, a HIT specification can be instantiated any number of times. Each time, a blank HIT instance with a new, unique set of Journey URLs will be generated.
Note the subtle distinction between HIT specification and HIT instance. Strictly, using Covfee involves creating HIT specifications (generic templates). Covfee translates these internally into HIT instances, which are concrete HITs, with resolved URLs attached to their Journeys. In other words, researchers work with HIT specifications, experiment subjects solve HIT instances.
In practice, we might use the term HIT to refer to both specifications and instances when the context is clear.
A Covfee Project may contain multiple different HIT specifications. A common case is to specify a HIT per experimental condition. In summary the following is the hierarchy used in Covfee, with examples for a Project, HIT, Journey and Task:
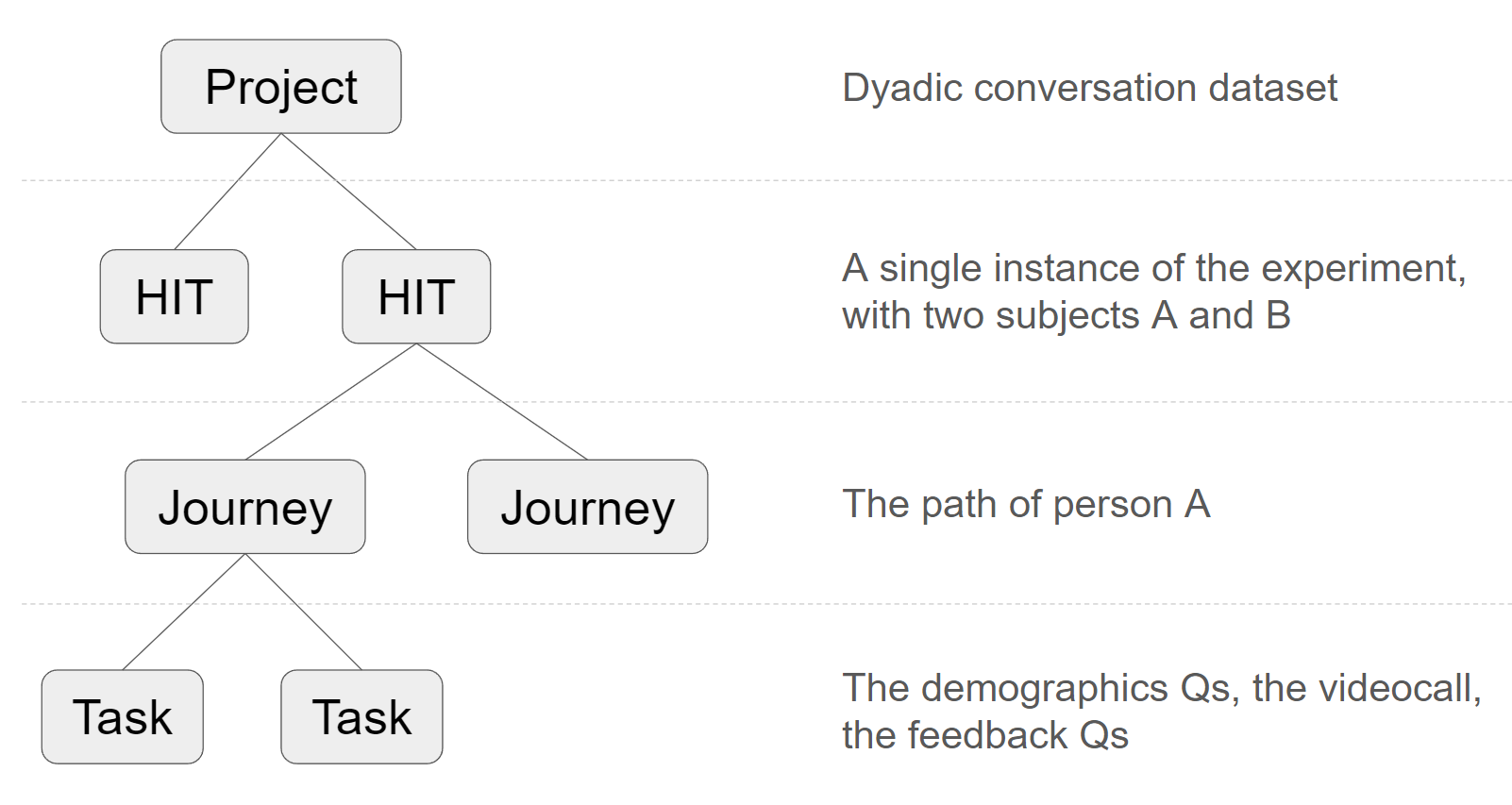
Finally, a Covfee app may also contain multiple independent Projects.